In This article reviews the Most Effective MQL5 Strategies Favored by Proprietary Trading Firms, emphasizing frameworks engineered to amplify returns without exceeding risk tolerances.
Across a spectrum of styles—trend following, swing trading, high-frequency scalping, grid methodologies, and event-driven approaches predicated on economic news
These systems serve as cornerstones for proprietary environments aspiring to cultivate replicable performance, stringent risk control, and durable temporal competitiveness.
Key Points & Best Mql5 Strategies Prop Firm List
| MQL5 Strategy | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Grid Trading EA | Uses grid system; works best in ranging markets; requires good risk management. |
| Trend Following Strategy | Captures big moves; uses indicators like MA, MACD; suited for strong trending markets. |
| Scalping EA | Executes quick trades on small price movements; needs low spreads and fast execution. |
| Martingale Strategy | Increases lot size after losses; high risk, high reward; requires strong capital buffer. |
| Breakout Trading | Enters positions when price breaks support/resistance; ideal during high volatility. |
| Arbitrage EA | Exploits price differences between brokers; requires fast execution; low-risk but limited availability. |
| Hedging Strategy | Uses opposite trades to minimize losses; reduces drawdowns; works well in uncertain markets. |
| News Trading EA | Trades based on economic news events; high volatility strategy; requires strong VPS setup. |
| Swing Trading Strategy | Holds trades for days/weeks; based on chart patterns and indicators; lower stress trading. |
| Mean Reversion Strategy | Assumes price returns to average; effective in sideways markets; needs careful stop-loss setup. |
10 Best Mql5 Strategies Prop Firm
1.Grid Trading EA
The Grid Trading EA adopts a systematic approach to price action by arranging limit orders at predetermined price intervals, effectively constructing an even grid of positions. This model excels in horizontal or consolidating markets, deriving profit from marginal price shifts within a confined range.
Despite its mechanical appeal, the strategy demands rigorous risk protocols; persistent directional moves can generate exponential drawdown. To accommodate prop-firm metrics, algorithms integrate strict exposure ceilings and auto-liquidation triggers, ensuring equity is not unduly compromised.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Works well in ranging markets | High drawdowns in strong trends |
| Generates frequent small profits | Requires large capital buffer |
| Automated and systematic approach | Complex risk management |
| Suitable for passive income | Can wipe account if unmanaged |
2.Trend Following Strategy
The Trend Following Strategy methodically leverages persistent directional behavior by deploying filters based on Multiple Moving Averages, MACD, or ADX to confirm prevailing momentum.
The entry is executed only upon the validation of robust directional indices, permitting the capture of protracted market relocations. Proprietary trading desks endorse the approach for its demonstrable asymmetry in large, sustained market trends.
Discipline in position management is paramount, as the strategy counsels the retention of winner trades at the expense of loss cut complacency, thus optimizing distance-to-profit metrics in favorable volatility environments.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Captures big market moves | Poor performance in sideways markets |
| Easy to automate with indicators | Late entries and exits common |
| Long-term consistency in trending phases | Requires patience and discipline |
| Popular and well-tested strategy | Risk of false signals |
3.Scalping EA
The Scalping EA caters to those who capture nominal price changes via rapid entries and exits. The paradigm flourishes with brokers offering ultra-narrow spreads, instantaneous execution, and high levels of depth. Although individual gains are modest, compounding multiple executions per day cumulates to a sizeable performance differential.
Consequently, proprietary trading desks frequently allocate short-term, quota-oriented accounts to scalping algorithms. However, tight foreign-exchange risk and technical latency impose non-negotiable limits; thus, a purpose-built
latched virtual-server-infrastructure (VPS) node is indispensable to manuscript profit. Mitigating slippage occurrences, excessive turnover, and potential long-tailed risk emerging from stop-loss or slippage rejections becomes a prior focus.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Generates quick, frequent profits | High stress and monitoring needed |
| Works well in liquid markets | Sensitive to spreads and slippage |
| Multiple opportunities daily | Requires fast execution (VPS) |
| Compounds profits effectively | Broker restrictions possible |
4.Martingale Strategy
The Martingale operational framework escalates nominal notional exposure after a succession of negative outcomes with the singular objective of covering cumulative shortfalls on the next favorable execution. Although ponderable historical performance tends to align with short-term equity recovery, intrinsic asymmetry permits catastrophic series risk.
Proprietary firms homologate the methodology within highly prescriptive and deterministic confident limits, measuring drawdown-to-capital responsiveness.
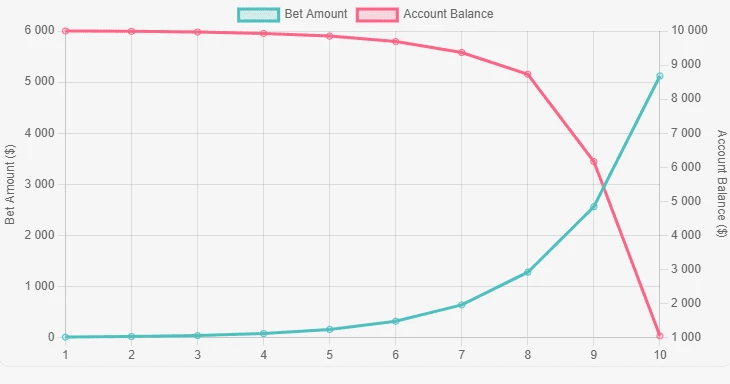
To engender sustainable capacity and defer the catastrophic-killing event, stringent equity thresholds, mandatory stop losses, and discretionary redeemable capital buffers are privileged.
When enforced with unwavering discipline, the Martingale device can indeed articulate contracted profit, yet the slightest deviation from the discipline path triggers hypertrophy of account annihilation.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Quick recovery of losses | Very high risk of large drawdowns |
| Simple to implement | Requires huge capital buffer |
| Can deliver steady short-term gains | Easily blows accounts in long trends |
| Works well in low-volatility ranges | Not suitable for strict prop firm rules |
5.Breakout Trading
The Breakout Trading methodology remains an extensively applied MQL5 algorithm that initiates positions upon decisive penetration of established support or resistance zones. The approach is designed for acceleration during high-volatility bursts—characteristic of session openings or the release of significant macroeconomic data.
Proprietary trading firms prefer this paradigm because the capacity to capture substantial intraday price displacement within constrained horizons aligns with their return targets. The predominant risk is the occurrence of false breakouts, which generate material drawdowns.

Practitioners mitigate the risk through the integration of concurrent volume verification, dynamic volatility measures, and rigorously calibrated stop-loss assemblages, collectively enhancing the risk return profile.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Captures large, fast moves | Risk of false breakouts |
| Works well in volatile markets | Stop-losses often triggered prematurely |
| Simple to understand | Requires strong timing and filters |
| Can be automated easily | High slippage during spikes |
6.Arbitrage EA
The Arbitrage EA exploits transient price mismatches across broker or exchange venues by simultaneously executing inverse sides of the trade, thereby hedging directional exposure and securing a predictive, coin-sized profit.
Such architectures demand near-millisecond order transmission, and latency thresholds, compelling proprietary desks to provision specialized colocated hardware with micro co-location configurations. Although the marginal profit per execution is modest, the high frequency of detectable discrepancies aggregates to a consistent absolute return stream.

Notwithstanding the statistically risk-neutral profile, liquidity venues frequently prohibit or severely curtail arbitrage sets, thereby institutionalising the discipline as a meticulously monitored edge that requires continual performance logging and redelivered parasitic technological support.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Low-risk profit opportunities | Brokers may ban arbitrage |
| Consistent if infrastructure is fast | Requires advanced tech setup |
| Market-neutral strategy | Limited availability of opportunities |
| Quick execution with low exposure | Profit per trade is small |
7.Hedging Strategy
The Hedging Strategy entails establishing a countervailing position to curtail overall risk exposure. Take, for instance, an active long position in EUR/USD, which the trader may offset by simultaneously initiating a short position whenever market uncertainty is pronounced.

Proprietary trading firms encourage the adoption of this approach since it tends to safeguard the trading capital in volatile conditions, thereby mitigating peak drawdowns. Maximum efficacy, however, is achieved only when the offsetting position is informed by disciplined market analysis
Which confirms the position will indeed counter the anticipated directional threat. Though hedging inherently caps participation in favorable price movements, the stability it affords justifies its frequent implementation alongside other tactical frameworks.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Reduces drawdowns | Limits profit potential |
| Provides protection during volatility | Requires higher margin |
| Helps preserve capital | Complex to manage effectively |
| Works across multiple instruments | Not allowed by all prop firms |
8.News Trading EA
The News Trading EA strategically exploits pronounced price fluctuations associated with forthcoming high-impact macroeconomic releases, including central-bank rate announcements and employment data.
Execution latency must be minimized to microseconds; hence a dedicated Vega-level VPS is mandated. While projected returns are elevated, adverse price behavior introduces equivalent exposure to slippage, expanding bid-ask spreads, and unforeseeable volatility.

Market-makers and proprietary desks alike deploy such EAs with rigorously narrowed risk limits and a full review of maximum hypothetical offset. When execution is within expected parameters, a single candle can yield meaningful risk-adjusted returns in sub-minute horizons, firmly placing this approach within the quintessence of high-precision intraday macro horizons.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| High-profit potential in seconds | Very high volatility risk |
| Capitalizes on economic events | Slippage and spread widening common |
| Works well with automation | Requires VPS for speed |
| Clear entry opportunities | Difficult to backtest accurately |
9.Swing Trading Strategy
Identified as a medium-horizon approach, Swing Trading is characterized by the holding of positions for intervals of multiple calendar days or weeks, thereby focusing on the capture of larger, nominal price oscillations.
Decision rules are a combination of quantitative technical overlays, manually identified price structure, and targeted risk-adjusted macro-fundamental overlays.

Proprietary desks deploy Swing Trading venues for its structural, asymptotic balance of value-at-risk relative to value-at-risk reward, marginal execution friction relative to intraday cracking, and muted psychological friction relative to high-frequency micro-scalping.
Optimal risk rewards are gained post-manifested price structure, with hinging stop-loss parameters and the ability to compartmentalize time being the most salient tactical qualifications for realized and ideal monetized exits.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Balanced risk and reward | Requires patience and time |
| Lower stress than scalping | Trades can last days/weeks |
| Works in trending and ranging markets | Vulnerable to overnight gaps |
| Suitable for part-time trading | Fewer trade opportunities |
10.Mean Reversion Strategy
Designed on the premise that price trajectories revert to statistically-determined means after reaching extremes, the Mean Reversion Strategy serves as a decision rule for momentary price exit.
Market practitioners frequently deploy volatility and momentum-based indicators, particularly Bollinger Bands and the Relative Strength Index (RSI), to delineate overbought and oversold thresholds.

Proprietary trading firms commonly espouse the technique within sideways markets, wherein assets exhibit a repetitive oscillatory path around a central tendency.
Although the structural premise frequently delivers results, adverse outcomes are both plausible and amplified during persistent directional trends; consequently, the discipline mandates subordinated stop-loss execution. Execution outcomes are optimally sharpened in concert with predefined capital management invariant.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Profitable in sideways markets | Fails in strong trends |
| Clear entry/exit signals | Requires strict stop-losses |
| Works well with indicators like RSI | High risk during breakouts |
| Provides frequent opportunities | Needs strong discipline |
Conclsuion
To conclude, the most effective MQL5 strategies for proprietary trading firms are determined by the individual trader’s style, risk appetite, and prevailing market dynamics.
Trend-following and swing trading systems are characterised by durability, delivering steady returns over extended periods, whereas scalping and news-based strategies generate immediate, albeit volatile, profits accompanied by elevated risk.
Grid and mean-reversion approaches are purposely designed for sideways markets, yet their success hinges on stringent risk management.
A diversification framework, wherein multiple methodologies are synchronised, mitigates the impact of single-system drawdowns and fosters balanced return profiles, thereby underpinning long-term capital preservation and progressive equity curves.
FAQ
Trend following or swing trading, as they are simple and low-stress.
Scalping EA and News Trading EA.
They are very risky and only suitable with strict risk controls
Grid Trading EA and Mean Reversion Strategy.







Leave a Reply